Number theory
Number theory is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers. Number theorists study prime numbers (which, when multiplied, give all the integers) as well as the properties of objects made out of integers (such as rational numbers) or defined as generalizations of the integers (such as, for example, algebraic integers).
Integers can be considered either in themselves or as solutions to equations (diophantine geometry). Questions in number theory are often best understood through the study of analytical objects (e.g., the Riemann zeta function) that encode properties of the integers, primes or other number-theoretic objects in some fashion (analytic number theory). One may also study real numbers in relation to rational numbers, e.g., as approximated by the latter (diophantine approximation).
The older term for number theory is arithmetic; by the early twentieth century,[1] it had been superseded by "number theory". (The word "arithmetic" is used by the general public to mean "elementary calculations"; it has also acquired other meanings in mathematical logic, as in Peano arithmetic, and computer science, as in floating point arithmetic.) The use of the term arithmetic for number theory regained some ground in the second half of the 20th century, arguably in part due to French influence.[2] In particular, arithmetical is preferred as an adjective to number-theoretic.
Contents |
History
Origins
Dawn of arithmetic
The first historical find of an arithmetical nature is a fragment of a table: the broken clay tablet Plimpton 322 (Larsa, Mesopotamia, ca. 1800 BCE) contains a list of "Pythagorean triples", i.e., integers 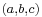 such that
such that 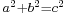 . The triples are too many and too large to have been obtained by brute force. The heading over the first column reads: "The takiltum of the diagonal which has been substracted such that the width..."[3]
. The triples are too many and too large to have been obtained by brute force. The heading over the first column reads: "The takiltum of the diagonal which has been substracted such that the width..."[3]
The table's outlay suggests[4] that it was constructed by means of what amounts, in modern language, to the identity
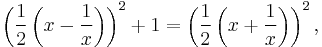
which is implicit in routine Old Babylonian exercises.[5] If some other method was used,[6] the triples were first constructed and then reordered by 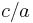 , presumably for actual use as a "table", i.e., with a view to applications.
, presumably for actual use as a "table", i.e., with a view to applications.
We do not know what these applications may have been, or whether there could have been any; Babylonian astronomy, for example, truly flowered only later. It has been suggested instead that the table was a source of numerical examples for school problems.[7][8]
While Babylonian number theory – or what survives of Babylonian mathematics that can be called thus – consists of this single, striking fragment, Babylonian algebra (in the secondary-school sense of "algebra") was exceptionally well developed.[9] Late Neoplatonic sources[10] state that Pythagoras learned mathematics from the Babylonians. (Much earlier sources[11] state that Thales and Pythagoras travelled and studied in Egypt.)
Euclid IX 21—34 is very probably Pythagorean;[12] it is very simple material ("odd times even is odd", "if an odd number measures [= divides] an even number, then it also measures [= divides] half of it"), but it is all that is needed to prove that 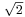 is irrational.[13] (Pythagoraean mystics gave great importance to the odd and the even.[14]) The discovery that
is irrational.[13] (Pythagoraean mystics gave great importance to the odd and the even.[14]) The discovery that 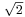 is irrational is credited to the early Pythagoreans (pre-Theodorus).[15] By revealing (in modern terms) that numbers could be irrational, this discovery seems to have provoked the first foundational crisis in mathematical history; its proof or its divulgation are sometimes credited to Hippasus, who was expelled or split from the Pythagorean sect.[16] It is only here that we can start to speak of a clear, conscious division between numbers (integers and the rationals – the subjects of arithmetic) and lengths (real numbers, whether rational or not).
is irrational is credited to the early Pythagoreans (pre-Theodorus).[15] By revealing (in modern terms) that numbers could be irrational, this discovery seems to have provoked the first foundational crisis in mathematical history; its proof or its divulgation are sometimes credited to Hippasus, who was expelled or split from the Pythagorean sect.[16] It is only here that we can start to speak of a clear, conscious division between numbers (integers and the rationals – the subjects of arithmetic) and lengths (real numbers, whether rational or not).
The Pythagorean tradition spoke also of so-called polygonal or figured numbers.[17] While square numbers, cubic numbers, etc., are seen now as more natural than triangular numbers, square numbers, pentagonal numbers, etc., the study of the sums of triangular and pentagonal numbers would prove fruitful in the early modern period (17th to early 19th century).
We know of no clearly arithmetical material in ancient Egyptian or Vedic sources, though there is some algebra in both. The Chinese remainder theorem appears as an exercise [18] in Sun Zi's Suan Ching (also known as Sun Tzu's Mathematical Classic; 3rd, 4th or 5th century CE.[19]). (There is one important step glossed over in Sun Zi's solution:[20] it is the problem that was later solved by Āryabhaṭa's kuṭṭaka – see below.)
There is also some numerical mysticism in Chinese mathematics,[21] but, unlike that of the Pythagoreans, it seems to have led nowhere. Like the Pythagoreans' perfect numbers, magic squares have passed from superstition into recreation.
Classical Greece and the early Hellenistic period
Aside from a few fragments, the mathematics of Classical Greece is known to us either through the reports of contemporary non-mathematicians or through mathematical works from the early Hellenistic period.[22] In the case of number theory, this means, by and large, Plato and Euclid, respectively.
Plato had a keen interest in mathematics, and distinguished clearly between arithmetic and calculation. (By arithmetic he meant, in part, theorising on number, rather than what arithmetic or number theory have come to mean.) It is through one of Plato's dialogues—namely, Theaetetus – that we know that Theodorus had proven that 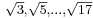 are irrational. Theaetetus was, like Plato, a disciple of Theodorus's; he worked on distinguishing different kind of inconmensurables, and was thus arguably a pioneer in the study of number systems. (Book X of Euclid's Elements is described by Pappus as being largely based on Theaetetus's work.)
are irrational. Theaetetus was, like Plato, a disciple of Theodorus's; he worked on distinguishing different kind of inconmensurables, and was thus arguably a pioneer in the study of number systems. (Book X of Euclid's Elements is described by Pappus as being largely based on Theaetetus's work.)
Euclid devoted part of his Elements to prime numbers and divisibility, topics that belong unambiguously to number theory and are basic thereto (Books VII to IX of Euclid's Elements). In particular, he gave an algorithm for computing the greatest common divisor of two numbers (the Euclidean algorithm; Elements, Prop. VII.2) and the first known proof of the infinitude of primes (Elements, Prop. IX.20).
In 1773, Lessing published an epigram he had found in a manuscript during his work as a librarian; it claimed to be a letter sent by Archimedes to Eratosthenes.[23] The epigram proposed what has become known as Archimedes' cattle problem; its solution (absent from the manuscript) requires solving an indeterminate quadratic equation (which reduces to what would later be misnamed Pell's equation). As far as we know, such equations were first successfully treated by the Indian school. It is not known whether Archimedes himself had a method of solution.
Diophantus
Very little is known about Diophantus of Alexandria; he probably lived in the third century CE, that is, about five hundred years after Euclid. Six out of the thirteen books of Diophantus's Arithmetica survive in the original Greek; four more books survive in an Arabic translation. The Arithmetica is a collection of worked-out problems where the task is invariably to find rational solutions to a system of polynomial equations, usually of the form 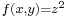 or
or 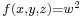 . Thus, nowadays, we speak of Diophantine equations when we speak of polynomial equations to which rational or integer solutions must be found.
. Thus, nowadays, we speak of Diophantine equations when we speak of polynomial equations to which rational or integer solutions must be found.
One may say that Diophantus was studying rational points—i.e., points whose coordinates are rational—on curves and algebraic varieties; however, unlike the Greeks of the Classical period, who did what we would now call basic algebra in geometrical terms, Diophantus did what we would now call basic algebraic geometry in purely algebraic terms. In modern language, what Diophantus does is to find rational parametrisations of many varieties; in other words, he shows how to obtain infinitely many rational numbers satisfying a system of equations by giving a procedure that can be made into an algebraic expression (say, 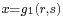 ,
, 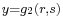 ,
, 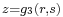 , where
, where 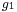 ,
, 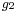 and
and 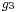 are polynomials or quotients of polynomials; this would be what is sought for if such
are polynomials or quotients of polynomials; this would be what is sought for if such 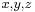 satisfied a given equation
satisfied a given equation 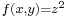 (say) for all values of r and s).
(say) for all values of r and s).
Diophantus also studies the equations of some non-rational curves, for which no rational parametrisation is possible. He manages to find some rational points on these curves – elliptic curves, as it happens, in what seems to be their first known occurrence—by means of what amounts to a tangent construction: translated into coordinate geometry (which did not exist in Diophantus's time), his method would be visualised as drawing a tangent to a curve at a known rational point, and then finding the other point of intersection of the tangent with the curve; that other point is a new rational point. (Diophantus also resorts to what could be called a special case of a secant construction.)
While Diophantus is concerned largely with rational solutions, he assumes some results on integer numbers; in particular, he seems to assume that every integer is the sum of four squares, though he never states as much explicitly.
Indian school: Āryabhaṭa, Brahmagupta, Bhāskara
While Greek astronomy – thanks to Alexander's conquests – probably influenced Indian learning, to the point of introducing trigonometry,[24] it seems to be the case that Indian mathematics is otherwise an indigenous tradition;[25] in particular, there is no evidence that Euclid's Elements reached India before the 18th century.[26]
Āryabhaṭa (476–550 CE) showed that pairs of simultaneous congruences 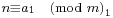 ,
, 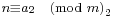 could be solved by a method he called kuṭṭaka, or pulveriser;[27] this is a procedure close to (a generalisation of) the Euclidean algorithm, which was probably discovered independently in India.[28] Āryabhaṭa seems to have had in mind applications to astronomical calculations.[29]
could be solved by a method he called kuṭṭaka, or pulveriser;[27] this is a procedure close to (a generalisation of) the Euclidean algorithm, which was probably discovered independently in India.[28] Āryabhaṭa seems to have had in mind applications to astronomical calculations.[29]
Brahmagupta (628 CE) started the systematic study of indefinite quadratic equations—in particular, the misnamed Pell equation, in which Archimedes may have first been interested, and which did not start to be solved in the West until the time of Fermat and Euler. Later Sanskrit authors would follow, using Brahmagupta's technical terminology. A general procedure (the chakravala, or "cyclic method") for solving Pell's equation was finally found by Jayadeva (cited in the eleventh century; his work is otherwise lost); the earliest surviving exposition appears in Bhāskara II's Bīja-gaṇita (twelfth century).[30]
Unfortunately, Indian mathematics remained largely unknown in the West until the late eighteenth century;[31] Brahmagupta and Bhāskara's work was translated (into English, by Colebrooke) in 1817.
Arithmetic in the Islamic golden age
In the early ninth century, the caliph Al-Ma'mun ordered translations of many Greek mathematical works and at least one Sanskrit work (the Sindhind, which may[32] or may not[33] be Brahmagupta's Brāhmasphuţasiddhānta), thus giving rise to the rich tradition of Islamic mathematics. Diophantus's main work, the Arithmetica, was translated into Arabic by Qusta ibn Luqa (820–912). Part of the treatise al-Fakhri (by al-Karajī, 953 – ca. 1029) builds on it to some extent. Al-Karajī's contemporary Ibn al-Haytham knew[34] what would later be called Wilson's theorem, which, arguably, was thus the first clearly non-trivial result on congruences to prime moduli ever known.
Other than a treatise on squares in arithmetic progression by Fibonacci – who lived and studied in north Africa and Constantinople during his formative years, ca. 1175–1200 – no number theory to speak of was done in western Europe while it went through the Middle Ages. Matters started to change in Europe in the late Renaissance, thanks to a renewed study of the works of Greek antiquity. A key catalyst was the textual emendation and translation into Latin of Diophantus's Arithmetica (Bachet, 1621, following a first attempt by Xylander, 1575).
Early modern number theory
Fermat
Pierre de Fermat (1601–1665) never published his writings; in particular, his work on number theory is contained entirely in letters to mathematicians and in private marginal notes.[35] He wrote down nearly no proofs in number theory; he had no models in the area.[36] He did make repeated use of mathematical induction, introducing the method of infinite descent.
One of Fermat's first interests was perfect numbers (which appear in Euclid, Elements IX) and amicable numbers;[37] this led him to work on integer divisors, which were from the beginning among the subjects of the correspondence (1636 onwards) that put him in touch with the mathematical community of the day.[38] He had already studied Bachet's edition of Diophantus carefully;[39] by 1643, his interests had shifted largely to diophantine problems and sums of squares[40] (also treated by Diophantus).
Fermat's achievements in arithmetic include:
- Fermat's little theorem (1640),[41] stating that, if a is not divisible by a prime p, then
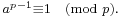 [42]
[42] - If a and b are coprime, then
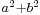 is not divisible by any prime congruent to −1 modulo 4.[43] Every prime congruent to −1 modulo 4 can be written in the form
is not divisible by any prime congruent to −1 modulo 4.[43] Every prime congruent to −1 modulo 4 can be written in the form 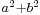 .[44] These statements date from 1640; in 1659, Fermat stated to Huygens that he had proven the latter statement by the method of descent.[45] Fermat and Frenicle also did some work (some of it erroneous or non-rigorous[46]) on other quadratic forms.
.[44] These statements date from 1640; in 1659, Fermat stated to Huygens that he had proven the latter statement by the method of descent.[45] Fermat and Frenicle also did some work (some of it erroneous or non-rigorous[46]) on other quadratic forms. - Fermat posed the problem of solving
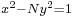 as a challenge to English mathematicians (1657). The problem was solved in a few months by Wallis and Brouncker.[47] Fermat considered their solution valid, but pointed out they had provided an algorithm without a proof (as had Jayadeva and Bhaskara, though Fermat would never know this). He states that a proof can be found by descent.
as a challenge to English mathematicians (1657). The problem was solved in a few months by Wallis and Brouncker.[47] Fermat considered their solution valid, but pointed out they had provided an algorithm without a proof (as had Jayadeva and Bhaskara, though Fermat would never know this). He states that a proof can be found by descent. - Fermat developed methods for (doing what in our terms amounts to) finding points on curves of genus 0 and 1. As in Diophantus, there are many special procedures and what amounts to a tangent construction, but no use of a secant construction.[48]
- Fermat states and proves in his correspondence[49] that
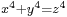 has no non-trivial solutions in the integers. Fermat also mentioned to his correspondents that
has no non-trivial solutions in the integers. Fermat also mentioned to his correspondents that 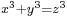 has no non-trivial solutions, and that this could be proven by descent.[50] The first known proof is due to Euler (1753; indeed by descent).[51]
has no non-trivial solutions, and that this could be proven by descent.[50] The first known proof is due to Euler (1753; indeed by descent).[51]
Fermat's claim ("Fermat's last theorem") to have shown there are no solutions to 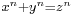 for all
for all 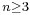 (a fact completely beyond his methods) appears only on his annotations on the margin of his copy of Diophantus; he never claimed this to others[52] and thus had no need to retract it if he found a mistake in his alleged proof.
(a fact completely beyond his methods) appears only on his annotations on the margin of his copy of Diophantus; he never claimed this to others[52] and thus had no need to retract it if he found a mistake in his alleged proof.
Euler
The interest of Leonhard Euler (1707–1783) in number theory was first spurred in 1729, when a friend of his, the amateur[53] Goldbach, pointed him towards some of Fermat's work on the subject.[54] This has been called the "rebirth" of modern number theory,[55] after Fermat's relative lack of success in getting his contemporaries' attention for the subject.[56] Euler's work on number theory includes the following:[57]
- Proofs for Fermat's statements. This includes Fermat's little theorem (generalised by Euler to non-prime moduli); the fact that
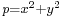 if and only if
if and only if 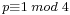 ; initial work towards a proof that every integer is the sum of four squares (the first complete proof is by Lagrange (1770), soon improved by Euler himself[58]); the lack of non-zero integer solutions to
; initial work towards a proof that every integer is the sum of four squares (the first complete proof is by Lagrange (1770), soon improved by Euler himself[58]); the lack of non-zero integer solutions to 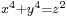 (implying the case n=4 of Fermat's last theorem, the case n=3 of which Euler also proved by a related method).
(implying the case n=4 of Fermat's last theorem, the case n=3 of which Euler also proved by a related method). - Pell's equation, first misnamed by Euler.[59] He wrote on the link between continued fractions and Pell's equation.[60]
- First steps towards analytic number theory. In his work of sums of four squares, partitions, pentagonal numbers, and the distribution of prime numbers, Euler pioneered the use of what can be seen as analysis (in particular, infinite series) in number theory. Since he lived before the development of complex analysis, most of his work is restricted to the formal manipulation of power series. He did, however, do some very notable (though not fully rigorous) early work on what would later be called the Riemann zeta function.[61]
- Quadratic forms. Following Fermat's lead, Euler did further research on the question of which primes are can be expressed in the form
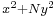 , some of it prefiguring quadratic reciprocity.[62]
, some of it prefiguring quadratic reciprocity.[62] - Diophantine equations. Euler worked on some diophantine equations of genus 0 and 1.[63] In particular, he studied Diophantus's work; he tried to systematise it, but the time was not yet ripe for such an endeavour – algebraic geometry was still in its infancy.[64] He did notice there was a connection between diophantine problems and elliptic integrals,[65] whose study he had himself initiated.
Lagrange, Legendre and Gauss
Lagrange (1736–1813) was the first to give full proofs of some of Fermat's and Euler's work and observations - for instance, the four-square theorem and the basic theory of the misnamed "Pell's equation" (for which an algorithmic solution was found by Fermat and his contemporaries, and also by Jayadeva and Bhaskara II before them). He also studied quadratic forms in full generality (as opposed to 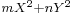 ) -- defining their equivalence relation, showing how to put them in reduced form, etc.
) -- defining their equivalence relation, showing how to put them in reduced form, etc.
Legendre (1752–1833) was the first to state the law of quadratic reciprocity. He also conjectured what amounts to the prime number theorem and Dirichlet's theorem on arithmetic progressions. He gave a full treatment of the equation 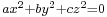 [66] and worked on quadratic forms along the lines later developed fully by Gauss.[67] In his old age, he was the first to prove "Fermat's last theorem" for
[66] and worked on quadratic forms along the lines later developed fully by Gauss.[67] In his old age, he was the first to prove "Fermat's last theorem" for 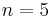 (completing work by Dirichlet, and crediting both him and Sophie Germain).[68]
(completing work by Dirichlet, and crediting both him and Sophie Germain).[68]
In Disquisitiones Arithmeticae (1798), Gauss (1777–1855) proved the law of quadratic reciprocity and developed the theory of quadratic forms (in particular, defining their composition). He also introduced some basic notation (congruences) and devoted a section to computational matters, including primality tests.[69] The last section of the Disquisitiones established a link between roots of unity and number theory:
The theory of the division of the circle…which is treated in sec. 7 does not belong by itself to arithmetic, but its principles can only be drawn from higher arithmetic.[70]
In this way, Gauss arguably made a first foray towards both Galois's work and algebraic number theory.
Maturity. Division into subfields.
Starting early in the nineteenth century, the following developments gradually took place:
- The rise to self-consciousness of number theory (or higher arithmetic) as a field of study.[71]
- The development of much of modern mathematics necessary for basic modern number theory: complex analysis, group theory, Galois theory—accompanied by greater rigor in analysis and abstraction in algebra.
- The rough subdivision of number theory into its modern subfields—in particular, analytic and algebraic number theory.
Algebraic number theory may be said to start with the study of reciprocity and cyclotomy, but truly came into its own with the development of abstract algebra and early ideal theory and valuation theory; see below. A conventional starting point for analytic number theory is Dirichlet's theorem on arithmetic progressions (1837),[72] whose proof introduced L-functions and involved some asymptotic analysis and a limiting process on a real variable.[73] The first use of analytic ideas in number theory actually goes back to Euler (1730s),[74] who used formal power series and non-rigorous (or implicit) limiting arguments. The use of complex analysis in number theory comes later: the work of Riemann (1859) on the zeta function is the canonical starting point;[75] Jacobi's four-square theorem (1839), which predates it, belongs to an initially different strand that has by now taken a leading role in analytic number theory (modular forms).[76]
The history of each subfield is briefly addressed in its own section below; see the main article of each subfield for fuller treatments. Many of the most interesting questions in each area remain open and are being actively worked on.
Main subdivisions
Elementary tools
The term elementary generally denotes a method that does not use complex analysis. For example, the prime number theorem was first proven in 1896, but an elementary proof was found only in 1949 by Erdős and Selberg.[77] The term is somewhat ambiguous: for example, proofs based on complex Tauberian theorems (e.g. Wiener–Ikehara) are often seen as quite enlightening but not elementary, in spite of using Fourier analysis, rather than complex analysis as such. Here as elsewhere, an elementary proof may be longer and more difficult for most readers than a non-elementary one.
Number theory has the reputation of being a field many of whose results can be stated to the layperson. At the same time, the proofs of these results are not particularly accessible, in part because the range of tools they use is, if anything, unusually broad within mathematics.[78]
Analytic number theory
Analytic number theory may be defined
- in terms of its tools, as the study of the integers by means of tools from real and complex analysis,[79]
- in terms of its concerns, as the study within number theory of estimates on size and density, as opposed to identities.[80]
Some subjects generally considered to be part of analytic number theory, e.g., sieve theory,[81] are better covered by the second rather than the first definition: some of sieve theory, for instance, uses little analysis,[82] yet it is considered to be part of analytic number theory.
The following are examples of problems in analytic number theory: the prime number theorem, the Goldbach conjecture (or the twin prime conjecture, or the Hardy–Littlewood conjectures), the Waring problem and the Riemann Hypothesis. Some of the most important tools of analytic number theory are the circle method, sieve methods and L-functions (or, rather, the study of their properties). The theory of modular forms (and, more generally, automorphic forms) also occupies an increasingly central place in the toolbox of analytic number theory.
One may ask analytic questions about algebraic numbers, and use analytic means to answer such questions; it is thus that algebraic and analytic number theory intersect. For example, one may define prime ideals (generalizations of prime numbers living in the field of algebraic numbers) and ask how many prime ideals there are up to a certain size. This question can be answered by means of an examination of Dedekind zeta functions, which are generalizations of the Riemann zeta function, an all-important analytic object that describes the distribution of prime numbers.
Algebraic number theory
Algebraic number theory studies algebraic properties and algebraic objects of interest in number theory. (Thus, analytic and algebraic number theory can and do overlap: the former is defined by its methods, the latter by its objects of study.) A key topic is that of the algebraic numbers, which are generalizations of the rational numbers. Briefly, an algebraic number is any complex number that is a solution to some polynomial equation 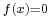 with rational coefficients; for example, every solution
with rational coefficients; for example, every solution  of
of 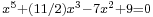 (say) is an algebraic number. Fields of algebraic numbers are also called algebraic number fields, or shortly number fields.
(say) is an algebraic number. Fields of algebraic numbers are also called algebraic number fields, or shortly number fields.
It could be argued that the simplest kind of number fields (viz., quadratic fields) were already studied by Gauss, as the discussion of quadratic forms in Disquisitiones arithmeticae can be restated in terms of ideals and norms in quadratic fields. (A quadratic field consists of all numbers of the form 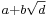 , where
, where 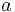 and
and 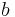 are rational numbers and
are rational numbers and 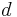 is a fixed rational number whose square root is not rational.) For that matter, the 11th-century chakravala method amounts—in modern terms—to an algorithm for finding the units of a real quadratic number field. However, neither Bhāskara nor Gauss knew of number fields as such.
is a fixed rational number whose square root is not rational.) For that matter, the 11th-century chakravala method amounts—in modern terms—to an algorithm for finding the units of a real quadratic number field. However, neither Bhāskara nor Gauss knew of number fields as such.
The grounds of the subject as we know it were set in the late nineteenth century, when ideal numbers, the theory of ideals and valuation theory were developed; these are three complementary ways of dealing with the lack of unique factorisation in algebraic number fields. (For example, in the field generated by the rationals and 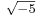 , the number
, the number 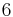 can be factorised both as
can be factorised both as 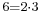 and
and 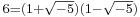 ; all of
; all of 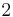 ,
, 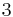 ,
, 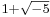 and
and 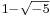 are irreducible, and thus, in a naïve sense, analogous to primes among the integers.) The initial impetus for the development of ideal numbers (by Kummer) seems to have come from the study of higher reciprocity laws,[83] i.e., generalisations of quadratic reciprocity.
are irreducible, and thus, in a naïve sense, analogous to primes among the integers.) The initial impetus for the development of ideal numbers (by Kummer) seems to have come from the study of higher reciprocity laws,[83] i.e., generalisations of quadratic reciprocity.
Number fields are often studied as extensions of smaller number fields: a field L is said to be an extension of a field K if L contains K. (For example, the complex numbers C are an extension of the reals R, and the reals R are an extension of the rationals Q.) Classifying the possible extensions of a given number field is a difficult and partially open problem. Abelian extensions—that is, extensions L of K such that the Galois group[84] Gal(L/K) of L over K is an abelian group—are relatively well understood. Their classification was the object of the programme of class field theory, which was initiated in the late 19th century (partly by Kronecker and Eisenstein) and carried out largely in 1900—1950.
An example of an active area of research in algebraic number theory is Iwasawa theory. The Langlands program, one of the main current large-scale research plans in mathematics, is sometimes described as an attempt to generalise class field theory to non-abelian extensions of number fields.
Diophantine geometry
The central problem of Diophantine geometry is to determine when a Diophantine equation has solutions, and if it does, how many. The approach taken is to think of the solutions of an equation as a geometric object.
For example, an equation in two variables defines a curve in the plane. More generally, an equation, or system of equations, in two or more variables defines a curve, a surface or some other such object in n-dimensional space. In Diophantine geometry, one asks whether there are any rational points (points all of whose coordinates are rationals) or integral points (points all of whose coordinates are integers) on the curve or surface. If there are any such points, the next step is to ask how many there are and how they are distributed. A basic question in this direction is: are there finitely or infinitely many rational points on a given curve (or surface)? What about integer points?
An example here may be helpful. Consider the Pythagorean equation 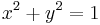 ; we would like to study its rational solutions, i.e., its solutions
; we would like to study its rational solutions, i.e., its solutions 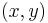 such that x and y are both rational. This is the same as asking for all integer solutions to
such that x and y are both rational. This is the same as asking for all integer solutions to 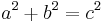 ; any solution to the latter equation gives us a solution
; any solution to the latter equation gives us a solution 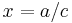 ,
, 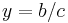 to the former. It is also the same as asking for all points with rational coordinates on the curve described by
to the former. It is also the same as asking for all points with rational coordinates on the curve described by 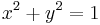 . (This curve happens to be a circle of radius 1 around the origin.)
. (This curve happens to be a circle of radius 1 around the origin.)
The rephrasing of questions on equations in terms of points on curves turns out to be felicitous. The finiteness or not of the number of rational or integer points on an algebraic curve—that is, rational or integer solutions to an equation 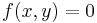 , where
, where  is a polynomial in two variables—turns out to depend crucially on the genus of the curve. The genus can be defined as follows:[85] allow the variables in
is a polynomial in two variables—turns out to depend crucially on the genus of the curve. The genus can be defined as follows:[85] allow the variables in 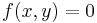 to be complex numbers; then
to be complex numbers; then 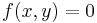 defines a 2-dimensional surface in (projective) 4-dimensional space (since two complex variables can be decomposed into four real variables, i.e., four dimensions). Count the number of (doughnut) holes in the surface; call this number the genus of
defines a 2-dimensional surface in (projective) 4-dimensional space (since two complex variables can be decomposed into four real variables, i.e., four dimensions). Count the number of (doughnut) holes in the surface; call this number the genus of 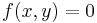 . Other geometrical notions turn out to be just as crucial.
. Other geometrical notions turn out to be just as crucial.
There is also the closely linked area of diophantine approximations: given a number  , how well can it be approximated by rationals? (We are looking for approximations that are good relative to the amount of space that it takes to write the rational: call
, how well can it be approximated by rationals? (We are looking for approximations that are good relative to the amount of space that it takes to write the rational: call 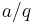 (with
(with 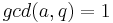 ) a good approximation to
) a good approximation to  if
if 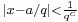 , where
, where 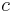 is large.) This question is of special interest if
is large.) This question is of special interest if  is an algebraic number. If
is an algebraic number. If  cannot be well approximated, then some equations do not have integer or rational solutions. Moreover, several concepts (especially that of height) turn out to be crucial both in diophantine geometry and in the study of diophantine approximations.
cannot be well approximated, then some equations do not have integer or rational solutions. Moreover, several concepts (especially that of height) turn out to be crucial both in diophantine geometry and in the study of diophantine approximations.
Diophantine geometry should not be confused with the geometry of numbers, which is a collection of graphical methods for answering certain questions in algebraic number theory. Arithmetic geometry, on the other hand, is a contemporary term for much the same domain as that covered by the term diophantine geometry. The term arithmetic geometry is arguably used most often when one wishes to emphasise the connections to modern algebraic geometry (as in, for instance, Faltings' theorem) rather than to techniques in diophantine approximations.
Recent approaches and subfields
The areas below date as such from no earlier than the mid-twentieth century, even if they are based on older material. For example, as is explained below, the matter of algorithms in number theory is very old, in some sense older than the concept of proof; at the same time, the modern study of computability dates only from the 1930s and 1940s, and computational complexity from the 1970s.
Probabilistic number theory
Take a number at random between one and a million. How likely is it to be prime? This is just another way of asking how many primes there are between one and a million. Very well; ask further: how many prime divisors will it have, on average? How many divisors will it have altogether, and with what likelihood? What is the probability that it have many more or many fewer divisors or prime divisors than the average?
Much of probabilistic number theory can be seen as an important special case of the study of variables that are almost, but not quite, mutually independent. For example, the event that a random integer between one and a million be divisible by two and the event that it be divisible by three are almost independent, but not quite.
It is sometimes said that probabilistic combinatorics uses the fact that whatever happens with probability greater than 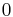 must happen sometimes; one may say with equal justice that many applications of probabilistic number theory hinge on the fact that whatever is unusual must be rare. If certain algebraic objects (say, rational or integer solutions to certain equations) can be shown to be in the tail of certain sensibly defined distributions, it follows that there must be few of them; this is a very concrete non-probabilistic statement following from a probabilistic one.
must happen sometimes; one may say with equal justice that many applications of probabilistic number theory hinge on the fact that whatever is unusual must be rare. If certain algebraic objects (say, rational or integer solutions to certain equations) can be shown to be in the tail of certain sensibly defined distributions, it follows that there must be few of them; this is a very concrete non-probabilistic statement following from a probabilistic one.
At times non-rigorous, probabilistic approach leads to a number of heuristic algorithms and open problems, notably Cramér's conjecture.
Arithmetic combinatorics
Let  be a set of integers. Consider the set
be a set of integers. Consider the set 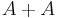 consisting of all sums of two elements of
consisting of all sums of two elements of  . Is
. Is 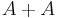 much larger than A? Barely larger? If
much larger than A? Barely larger? If 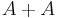 is barely larger than
is barely larger than  , must
, must  have plenty of arithmetic structure \pmod e.g., does it look like an arithmetic progression?
have plenty of arithmetic structure \pmod e.g., does it look like an arithmetic progression?
If we begin from a fairly "thick" infinite set  , does it contain many elements in arithmetic progression:
, does it contain many elements in arithmetic progression: 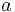 ,
, 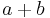 ,
, 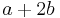 ,
, 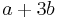 ,
,  ,
, 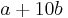 , say? Should it be possible to write large integers as sums of elements of
, say? Should it be possible to write large integers as sums of elements of  ?
?
These questions are characteristic of arithmetic combinatorics. This is a presently coalescing field; it subsumes additive number theory (which concerns itself with certain very specific sets  of arithmetic significance, such as the primes or the squares) and, arguably, some of the geometry of numbers, together with some rapidly developing new material. Its focus on issues of growth and distribution accounts in part for its developing links with ergodic theory, finite group theory, model theory, and other fields. The term additive combinatorics is also used; however, the sets
of arithmetic significance, such as the primes or the squares) and, arguably, some of the geometry of numbers, together with some rapidly developing new material. Its focus on issues of growth and distribution accounts in part for its developing links with ergodic theory, finite group theory, model theory, and other fields. The term additive combinatorics is also used; however, the sets  being studied need not be sets of integers, but rather subsets of non-commutative groups, for which the multiplication symbol, not the addition symbol, is traditionally used; they can also be subsets of rings, in which case the growth of
being studied need not be sets of integers, but rather subsets of non-commutative groups, for which the multiplication symbol, not the addition symbol, is traditionally used; they can also be subsets of rings, in which case the growth of 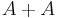 and
and  ·
· may be compared.
may be compared.
Computations in number theory
While the word algorithm goes back only to certain readers of al-Khwārizmī, careful descriptions of methods of solution are older than proofs: such methods (that is, algorithms) are as old as any recognisable mathematics—ancient Egyptian, Babylonian, Vedic, Chinese—whereas proofs appeared only with the Greeks of the classical period. An interesting early case is that of what we now call the Euclidean algorithm. In its basic form (namely, as an algorithm for computing the greatest common divisor) it appears as Proposition 2 of Book VII in Elements, together with a proof of correctness. However, in the form that is often used in number theory (namely, as an algorithm for finding integer solutions to an equation 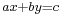 , or, what is the same, for finding the quantities whose existence is assured by the Chinese remainder theorem) it first appears in the works of Āryabhaṭa (5th–6th century CE) as an algorithm called kuṭṭaka ("pulveriser"), without a proof of correctness.
, or, what is the same, for finding the quantities whose existence is assured by the Chinese remainder theorem) it first appears in the works of Āryabhaṭa (5th–6th century CE) as an algorithm called kuṭṭaka ("pulveriser"), without a proof of correctness.
There are two main questions: "can we compute this?" and "can we compute it rapidly?". Anybody can test whether a number is prime or, if it is not, split it into prime factors; doing so rapidly is another matter. We now know fast algorithms for testing primality, but, in spite of much work (both theoretical and practical), no truly fast algorithm for factoring.
The difficulty of a computation can be useful: modern protocols for encrypting messages (e.g., RSA) depend on functions that are known to all, but whose inverses (a) are known only to a chosen few, and (b) would take one too long a time to figure out on one's own. For example, these functions can be such that their inverses can be computed only if certain large integers are factorized. While many difficult computational problems outside number theory are known, most working encryption protocols nowadays are based on the difficulty of a few number-theoretical problems.
On a different note—some things may not be computable at all; in fact, this can be proven in some instances. For instance, in 1970, it was proven that there is no Turing machine which can solve all Diophantine equations (see Hilbert's 10th problem). There are thus some problems in number theory that will never be solved. We even know the shape of some of them, viz., Diophantine equations in nine variables; we simply do not know, and cannot know, which coefficients give us equations for which the following two statements are both true: there are no solutions, and we shall never know that there are no solutions.
Literature
Two of the most popular introductions to the subject are:
- G. H. Hardy and E. M. Wright, An introduction to the theory of numbers, 6th ed., rev. by D. R. Heath-Brown and J. H. Silverman, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2008 (first published in 1938).
- I. M. Vinogradov, Elements of Number Theory, Mineola, NY: Dover Publications, 2003, reprint of the 1954 edition.
Hardy and Wright's book is a comprehensive classic, though its clarity sometimes suffers due to the authors' insistence on elementary methods.[86] Vinogradov's main attraction consists in its set of problems, which quickly lead to Vinogradov's own research interests; the text itself is very basic and close to minimal.
Popular choices for a second textbook include:
- Borevich, A. I.; Shafarevich, Igor R. (1966), Number theory, Pure and Applied Mathematics, 20, Boston, MA: Academic Press, ISBN 978-0-12-117850-5, MR0195803, http://books.google.com/books?id=njgVUjjO-EAC
- Jean-Pierre Serre, A Course in Arithmetic, Graduate Texts in Mathematics, Springer Verlag, (1996, ISBN 978-0-387-90040-7)
See also
References
- ^ By 1921, T. L. Heath had to explain: "By arithmetic Plato meant, not arithmetic in our sense, but the science which considers numbers in themselves, in other words, what we mean by the Theory of Numbers." In: Sir Thomas Heath, A History of Greek Mathematics, vol. 1, Dover, 1981, p. 13.
- ^ Take, e.g., Serre's A Course in Arithmetic (1970; translated into English in 1973). In 1952, Davenport still had to specify that he meant The Higher Arithmetic. Hardy and Wright wrote in the introduction to An Introduction to the Theory of Numbers (1938): "We proposed at one time to change [the title] to An introduction to arithmetic, a more novel and in some ways a more appropriate title; but it was pointed out that this might lead to misunderstandings about the content of the book."
- ^ Neugebauer and Sachs, Mathematical cuneiform texts, American Oriental Series, Vol. 29, 1945, p. 40. The term takiltum is problematic. Robson (E. Robson, "Neither Sherlock Holmes nor Babylon: a reassessment of Plimpton 322", Historia Math. 28 (3), p. 192) prefers the rendering "The holding-square of the diagonal from which 1 is torn out, so that the short side comes up...".
- ^ Robson, op. cit., p. 189. Other sources give the modern formula
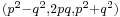 . Van der Waerden, Science Awakening, Oxford University Press, New York, 1961, p. 79, gives both the modern formula and what amounts to the form preferred by Robson.
. Van der Waerden, Science Awakening, Oxford University Press, New York, 1961, p. 79, gives both the modern formula and what amounts to the form preferred by Robson. - ^ Robson, op. cit., p. 184.
- ^ Neugebauer (O. Neugebauer, The exact sciences in antiquity, Dover, 1969 (corrected preprint of the 1957 ed.), pp. 36–40) discusses the table in detail and mentions in passing Euclid's method in modern notation (Neugebauer, op. cit., p. 39)
- ^ J. Friberg, Methods and traditions of Babylonian mathematics: Plimpton 322, Pythagorean triples and the Babylonian triangle parameter equations, Historia Math. 8, p. 302.
- ^ Robson, op. cit., p. 201. This is controversial. See Plimpton 322. Robson's article is written polemically (Robson, op. cit., 202), with a view to "perhaps [...] knocking [Plimpton 322] off its pedestal" (Robson, op. cit., 167); at the same time, it settles to the conclusion that
[...] the question “how was the tablet calculated?” does not have to have the same answer as the question “what problems does the tablet set?” The first can be answered most satisfactorily by reciprocal pairs, as first suggested half a century ago, and the second by some sort of right-triangle problems.
(Robson, op. cit., 202). Robson takes issue with the notion that the scribe who produced Plimpton 322 (who had to "work for a living", and would not have belonged to a "leisured middle class") could have been motivated by his own "idle curiosity" in the absence of a "market for new mathematics" (Robson, op. cit., 199–200).
- ^ B. L. van der Waerden, Science awakening, Oxford University Press, New York, 1961, p. 43.
- ^ Iamblichus, Life of Pythagoras, cited in van der Waerden, op. cit., p. 108. See also Porphyry, Life of Pythagoras, paragraph 6, in Kenneth Sylvan Guthrie, The Pythagorean Sourcebook and Library, Phanes Press, 1987. Van der Waerden (op. cit., p. 87–90) sustains the view that Thales knew Babylonian mathematics.
- ^ Herodotus (II. 81) and Isocrates (Busiris 28), cited in: C. A. Huffman, "Pythagoras", Stanford Encyclopaedia of Philosophy. On Thales, see Eudemus ap. Proclus, 65.7, cited in: Patricia O'Grady, "Thales of Miletus", The Internet Encyclopaedia of Philosophy.
- ^ O. Becker, Quellen und Studien, B 4, p. 533, cited in: van der Waerden, op. cit., p. 108.
- ^ O. Becker, op. cit.
- ^ van der Waerden, op. cit., p. 109.
- ^ Plato, Theaetetus, p. 147 B, cited in: Kurt von Fritz, "The discovery of incommensurability by Hippasus of Metapontum", p. 212, in: J. Christianidis (ed.), Classics in the History of Greek Mathematics, Kluwer, 2004.
- ^ von Fritz, op. cit.
- ^ T. Heath, A History of Greek Mathematics: From Thales to Euclid, vol. 1, Dover, 1981, p. 76.
- ^ Sun Zi, Suan Ching, Chapter 3, Problem 26. This can be found in pp. 219–220 of Lam Lay Yong and Ang Tian Se, Fleeting Footsteps: Tracing the conception of arithmetic and algebra in ancient China, rev. ed., World Scientific, 2004, which contains a full translation of the Suan Ching (based on Qian Baocong (ed.) Suanjing shi shu (Ten mathematical classics). Beijing: Zhonghua shuju, 1963). See also the discussion in Yong and Se, op. cit., pp. 138–140.
- ^ The date of the text has been narrowed down to 220–420 AD (Yan Dunjie) or 280–473 AD (Wang Ling) due to internal evidence (= taxation systems assumed in the text). See Yong and Se, op. cit., pp. 27–28.
- ^ Sun Zi, Suan Ching, Ch. 3, Problem 26, in Yong and Se, op. cit., pp. 219–220:
[26] Now there are an unknown number of things. If we count by threes, there is a remainder 2; if we count by fives, there is a remainder 3; if we count by sevens, there is a remainder 2. Find the number of things. Answer: 23. Method: If we count by threes and there is a remainder 2, put down 140. If we count by fives and there is a remainder 3, put down 63. If we count by sevens and there is a remainder 2, put down 30. Add them to obtain 233 and subtract 210 to get the answer. If we count by threes and there is a remainder 1, put down 70. If we count by fives and there is a remainder 1, put down 21. If we count by sevens and there is a remainder 1, put down 15. When [a number] exceeds 106, the result is obtained by subtracting 105.
- ^ See, e.g., Sun Zi, Suan Ching, Ch. 3, Problem 36, in Yong and Se, op. cit., pp. 223–224:
[36] Now there is a pregnant woman whose age is 29. If the gestation period is 9 months, determine the sex of the unborn child. Answer: Male. Method: Put down 49, add the gestation period and subtract the age. From the remainder take away 1 representing the heaven, 2 the earth, 3 the man, 4 the four seasons, 5 the five phases, 6 the six pitch-pipes, 7 the seven stars [of the Dipper], 8 the eight winds, and 9 the nine divisions [of China under Yu the Great]. If the remainder is odd, [the sex] is male and if the remainder is even, [the sex] is female.
This is the last problem in Sun Zi's otherwise matter-of-fact treatise.
- ^ See, e.g., C. Boyer, A History of Mathematics, 2nd. ed., revised by Merzbach, Wiley, 1991, p. 82.
- ^ Vardi, I., "Archimedes' cattle problem", American Mathematical Monthly, v. 105, n. 4, pp. 305–319. See also Weil, op. cit., pp. 17–24.
- ^ K. Plofker, op. cit., p. 134
- ^ Any early contact between Babylonian and Indian mathematics remains conjectural (K. Plofker, op. cit., p. 42).
- ^ D. Mumford, Mathematics in India: reviewed by David Mumford, Notices of the AMS, March 2010, p. 387.
- ^ Āryabhaṭa, Āryabhatīya, Chapter 2, verses 32–33, cited in: K. Plofker, Mathematics in India, Princeton University Press, 2008, pp. 134–140. See also W. E. Clark, The Āryabhaṭīya of Āryabhaṭa: An ancient Indian work on Mathematics and Astronomy, University of Chicago Press, 1930, pp. 42–50. A slightly more explicit description of the kuṭṭaka was later given in Brahmagupta, Brāhmasphuṭasiddhānta, XVIII, 3–5 (in Colebrooke, Algebra, with Arithmetic and Mensuration, from the Sanscrit of Brahmegupta and Bháscara, London, 1817, p. 325, cited in: Clark, op. cit., p. 42).
- ^ Mumford, op. cit., p. 388
- ^ Plofker, op. cit., p. 119.
- ^ Plofker, op. cit., p. 194
- ^ Plofker, op. cit., p. 283
- ^ Colebrook, op. cit., lxv, cited in J. F. P. Hopkins, Geographical and navigational literature, Ch. 17 of M. J. L. Young, J. D. Latham and R. B. Serjeant, eds., The Cambridge history of Arabic literature: Religion, learning and science in the `Abbasid period, Cambridge University Press, 1990, p. 302. See also the preface in E. Sachau, Alberuni's India: An account of the religion, philosophy, literature, geography, chronology, astronomy and astrology of India, Vol I, 1888, cited in: D. E. Smith, History of Mathematics, Vol I., Dover, 1958, p. 168.
- ^ D. Pingree, The fragments of the works of Ya'qub ibn Tariq, Journal of Near Eastern Studies 26, 1968, 97–125, and D. Pingree, The fragments of the works of al-Fazari, Journal of Near Eastern Studies 28, 1970, 103–123, cited in Plofker, op. cit., p. 256.
- ^ Roshdi Rashed, Ibn al-Haytham el le théorème de Wilson, Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 22 (1980), no. 4, pp. 305–321.
- ^ André Weil, Number theory: an approach through history – from Hammurapi to Legendre, Birkhäuser, 1984, pp. 45–46.
- ^ Weil, op. cit., p. 118. This was more so in number theory than in other areas (remark in M. S. Mahoney, The mathematical career of Pierre de Fermat, 1601–1665, Princeton Univ. Press, 1994, 2nd ed., p. 284). Bachet's own proofs were "ludicrously clumsy" (Weil, op. cit., p. 33).
- ^ Perfect and especially amicable numbers are of little or no interest nowadays. The same was not true in medieval times – whether in the West or the Arab-speaking world – due in part to the importance given to them by the Neopythagorean (and hence mystical) Nicomachus (ca. 100 CE), who wrote a primitive but influential "Introduction to Arithmetic". See Van der Waerden, Science Awakening, Oxford, 1961, Ch. IV.
- ^ Mahoney, op. cit., p. 48 and pp. 53–54. The initial subjects of Fermat's correspondence included divisors ("aliquot parts") and many subjects outside number theory; see the list in the letter from Fermat to Roberval, 22.IX.1636, Ch. Henry and Tannery (eds.), Oeuvres de Fermat, Paris, 1891-1912, vol. II, pp. 72 and 74, cited in: Mahoney, op. cit., p. 54.
- ^ Weil, op. cit., pp. 1–2.
- ^ Weil, op. cit., p. 53
- ^ Letter from Fermat to Frenicle, 1640, cited in: Weil, op. cit., p. 56
- ^ Here, as usual, given two integers a and b and a non-zero integer m, we write
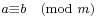 (read "a is congruent to b modulo m") to mean that m divides a&nsbp;− b, or, what is the same, a and b leave the same residue when divided by m. This notation is actually much later than Fermat's; it first appears in section 1 of Gauss's Disquisitiones Arithmeticae. Fermat's little theorem is a consequence of the fact that the order of an element of a group divides the order of the group. The modern proof would have been within Fermat's means (and was indeed given later by Euler), even though the modern concept of a group came long after Fermat or Euler. (It helps to know that inverses exist modulo p (i.e., given a not divisible by a prime p, there is an integer x such that
(read "a is congruent to b modulo m") to mean that m divides a&nsbp;− b, or, what is the same, a and b leave the same residue when divided by m. This notation is actually much later than Fermat's; it first appears in section 1 of Gauss's Disquisitiones Arithmeticae. Fermat's little theorem is a consequence of the fact that the order of an element of a group divides the order of the group. The modern proof would have been within Fermat's means (and was indeed given later by Euler), even though the modern concept of a group came long after Fermat or Euler. (It helps to know that inverses exist modulo p (i.e., given a not divisible by a prime p, there is an integer x such that 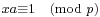 ); this fact (which, in modern language, makes the residues mod p into a group, and which was already known to Āryabhaṭa; see above) was familiar to Fermat thanks to its rediscovery by Bachet (Weil, op. cit., p. 7). Weil goes on to say that Fermat would have recognised that Bachet's argument is essentially Euclid's algorithm.
); this fact (which, in modern language, makes the residues mod p into a group, and which was already known to Āryabhaṭa; see above) was familiar to Fermat thanks to its rediscovery by Bachet (Weil, op. cit., p. 7). Weil goes on to say that Fermat would have recognised that Bachet's argument is essentially Euclid's algorithm. - ^ P. de Fermat, Varia Opera Mathematica D. Petri de Fermat Senatoris Tolosani... Tolosae, Apud Joannem Pech... juxta Collegium PP. Societatis Jesu M.DC.LXXIX, ch. II, 204, cited in: Weil, op. cit., p. 63. All of the following citations from Fermat's Varia Opera are taken from Weil, op. cit., ch. II.
- ^ Fermat, op. cit., II.213.
- ^ Fermat, op. cit., II.423.
- ^ Weil, op. cit., 80; Weil, op. cit., 91–92.
- ^ Weil, op. cit., p. 92.
- ^ Weil, op. cit., Ch. II, sections XV and XVI.
- ^ Fermat, op. cit., I. 340–341, Obs. XLV; by descent
- ^ Weil, op. cit., p. 115
- ^ Weil, op. cit., 115–116.
- ^ Weil, op. cit., p. 104
- ^ Up to the second half of the seventeenth century, academic positions were very rare, and most mathematicians and scientists earned their living in some other way (Weil, op. cit., p. 159 and p. 161). (There were already some recognisable features of professional practice, viz., seeking correspondents, visiting foreign colleagues, building private libraries (Weil, op. cit. 160–161).) Matters started to shift in the late 17th century (Weil, op. cit., 161); scientific academies were founded in England (the Royal Society, 1662) and France (the Académie des sciences, 1666) and Russia (1724). Euler was offered a position at this last one in 1726; he accepted, arriving in St. Petersburg in 1727. (Weil, op. cit., p. 163, and V. S. Varadarajan, Euler through time: a new look at old themes, AMS, 2006, p. 7). In this context, the term amateur usually applied to Goldbach is well-defined and makes some sense: he has been described as a man of letters who earned a living as a spy (C. A. Truesdell, Leonard Euler, supreme geometer, introduction to L. Euler, Elements of Algebra, translated from German by John Hewlett, reprint of the 1840 edition, with an introduction by C. Truesdell, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1984, p. xv; cited in Varadarajan, op. cit., p. 9). Notice, however, that Goldbach published some works on mathematics and sometimes held academic positions.
- ^ Weil, op. cit., p. 2 and p. 172, and Varadarajan, op. cit., p. 9.
- ^ Weil, op. cit., pp. 1 and 2.
- ^ Weil, op. cit., p. 2, and Varadarajan, op. cit., p. 37
- ^ Varadarajan, op. cit., p. 39, and Weil, op. cit., pp. 176–189.
- ^ Weil, op. cit., pp. 178–179
- ^ Weil, op. cit., p. 174. Euler was generous in giving credit to others (Varadarajan, op. cit., p. 14), not always correctly.
- ^ Weil, op. cit., p. 183
- ^ Varadarajan, op. cit., pp. 48–55; see also chapter III.
- ^ Varadarajan, op. cit., pp. 44–47; Weil, op. cit., pp. 177–179; H. M. Edwards, "Euler and quadratic reciprocity", Math. Magazine, 56 (November 1983), 285–291.
- ^ Varadarajan, op. cit., 55–56, and Weil, op. cit., pp. 179–181
- ^ Weil, op. cit., p. 181.
- ^ Weil, op. cit., p. 181
- ^ Weil, op. cit., pp. 327–328.
- ^ Weil, op. cit., pp. 332–334.
- ^ Weil, op. cit., pp. 337–338.
- ^ C. Goldstein and N. Schappacher, "A book in search of a discipline", in: C. Goldstein, N. Schappacher and J. Schwermer (eds.), The Shaping of Arithmetic, Springer, 2007, p. 14.
- ^ From the preface of Disquisitiones Arithmeticae; the translation is taken from Goldstein and Schappacher, op. cit., p. 16.
- ^ See the discussion in section 5 of C. Goldstein and N. Schappacher, "A book in search of a discipline (1801–1860)', in C. Goldstein, N. Schappacher and J. Schwermer (eds.), "The shaping of arithmetic after C. F. Gauss's Disquisitiones Arithmeticae", Springer, 2007. Early signs of self-consciousness are present already in letters by Fermat: thus his remarks on what number theory is, and how "Diophantus's work [...] does not really belong to [it]" (quoted in A. Weil, op. cit., p. 25).
- ^ See T. Apostol, Introduction to analytic number theory, Springer, 1976, p. 7, and H. Davenport, Multiplicative number theory, Markham, Chicago, 1967, p. 1.
- ^ See the proof in Davenport, op. cit., section 1.
- ^ H. Iwaniec and E. Kowalski, Analytic number theory, AMS Colloquium Publications, vol. 53, AMS, Providence, 2004, p. 1; see also Varadarajan, op. cit., sections 2.5, 3.1 and 6.1.
- ^ A. Granville, "Analytic number theory", section 3, in: T. Gowers et al. (eds.), The Princeton Companion to to Mathematics, Princeton University Press, 2008, pp. 322-348.
- ^ See the comment on the importance of modularity in Iwaniec and Kowalski, op. cit., p. 1
- ^ D. Goldfeld, Elementary proof of the prime number theorem. A historical perspective.
- ^ See, e.g., the initial comment in Iwaniec and Kowalski, op. cit., p. 1.
- ^ Apostol, op. cit., p. 7
- ^ Granville, op. cit., section 1: "The main difference is that in algebraic number theory [...] one typically considers questions with answers that are given by exact formulas, whereas in analytic number theory [...] one looks for good approximations."
- ^ Sieve theory figures as one of the main subareas of analytic number theory in many standard treatments; see, for instance, Iwaniec and Kowalski, op. cit., or H. Montgomery and R. Vaughan, Multiplicative number theory, I. Classical Theory, Cambridge, 2007
- ^ This is the case for small sieves (in particular, some combinatorial sieves such as the Brun sieve) rather than for large sieves; the study of the latter now includes ideas from harmonic and functional analysis.
- ^ H. M. Edwards, Fermat's Last Theorem: a genetic introduction to algebraic number theory, Springer Verlag, 1977, p. 79.
- ^ The Galois group of an extension K/L consists of the operations (isomorphisms) that send elements of L to other elements of L while leaving all elements of K fixed. Thus, for instance, Gal(C/R) consists of two elements: the identity element (taking every element x + iy of C to itself) and complex conjugation (the map taking each element x + iy to x − iy). The Galois group of an extension tells us many of its crucial properties. The study of Galois groups started with Évariste Galois; in modern language, the main outcome of his work is that an equation f(x) = 0 can be solved by radicals (that is, x can be expressed in terms of the four basic operations together with square roots, cubic roots, etc.) if and only if the extension of the rationals by the roots of the equation f(x) = 0 has a Galois group that is solvable in the sense of group theory. ("Solvable", in the sense of group theory, is a simple property that can be checked easily for finite groups.)
- ^ It may be useful to look at an example here. Say we want to study the curve
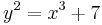 . We allow x and y to be complex numbers:
. We allow x and y to be complex numbers: 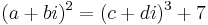 . This is, in effect, a set of two equations on four variables, since both the real and the imaginary part on each side must match. As a result, we get a surface (two-dimensional) in four dimensional space. After we choose a convenient hyperplane on which to project the surface (meaning that, say, we choose to ignore the coordinate a), we can plot the resulting projection, which is a surface in ordinary three-dimensional space. It then becomes clear that the result is a torus, i.e., the surface of a doughnut (somewhat stretched). A doughnut has one hole; hence the genus is 1.
. This is, in effect, a set of two equations on four variables, since both the real and the imaginary part on each side must match. As a result, we get a surface (two-dimensional) in four dimensional space. After we choose a convenient hyperplane on which to project the surface (meaning that, say, we choose to ignore the coordinate a), we can plot the resulting projection, which is a surface in ordinary three-dimensional space. It then becomes clear that the result is a torus, i.e., the surface of a doughnut (somewhat stretched). A doughnut has one hole; hence the genus is 1. - ^ T. M. Apostol, Review of An introduction to the theory of numbers, Mathematical Reviews, MR0568909.
This article incorporates material from the Citizendium article "Number theory", which is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License but not under the GFDL.
External links
|
|||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||